
The white-throated hummingbird is a species of hummingbird in the "emeralds", tribe Trochilini of subfamily Trochilinae. It is found in Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay.
Region
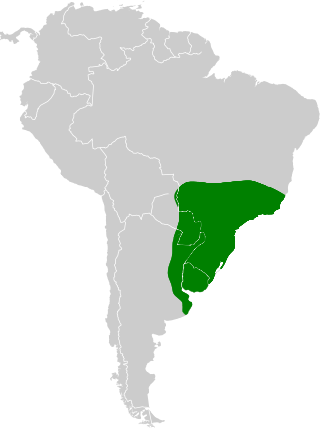
Southeastern South America
Typical Environment
Found from eastern and southern Brazil through Paraguay and Uruguay into northeastern Argentina. It thrives in forest edges, secondary growth, gallery woodlands, and coastal restinga, and is also frequent in parks, gardens, and plantations. The species tolerates human-modified landscapes where flowering plants are abundant. It generally avoids dense interior forest and very open treeless habitats.
Altitude Range
Sea level to 1500 m
Climate Zone
Subtropical
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 1/5
This medium-sized hummingbird is common in gardens and forest edges across southeastern South America and readily visits feeders and flowering shrubs. It fiercely defends nectar sources, chasing off rivals with rapid aerial pursuits. Its cup-shaped nest is made of plant down and spider silk, often placed on a horizontal branch under sheltering leaves. By visiting a wide range of flowers, it acts as an important pollinator in the Atlantic Forest biome.




Temperament
territorial and energetic
Flight Pattern
short rapid wingbeats with sustained hovering and swift darting chases
Social Behavior
Typically solitary at flowers, with males aggressively defending feeding territories. During breeding, the female builds a small cup nest of plant fibers and spider silk and alone incubates and feeds the young. Courtship involves chases and display flights around nectar sources.
Migratory Pattern
Partial migrant
Song Description
Vocalizations are a series of thin, high-pitched chips and squeaky notes given while foraging or during chases. Wing hum is audible at close range and intensifies during aggressive interactions.
Plumage
Iridescent green upperparts with a pure white throat and breast, green-washed flanks, and darker bluish-green tail with pale tips. The underparts contrast sharply with the glittering green head and back. Plumage is sleek and glossy, especially in good light.
Diet
Primarily consumes nectar from a wide array of flowering shrubs and trees, including native and ornamental species. It supplements its diet with small arthropods captured by hawking or gleaning from foliage, providing essential protein. It may also visit sap wells created by woodpeckers when available.
Preferred Environment
Feeds along forest edges, gardens, and clearings where tubular flowers are abundant. Often returns repeatedly to defended flower patches and feeders within its territory.