
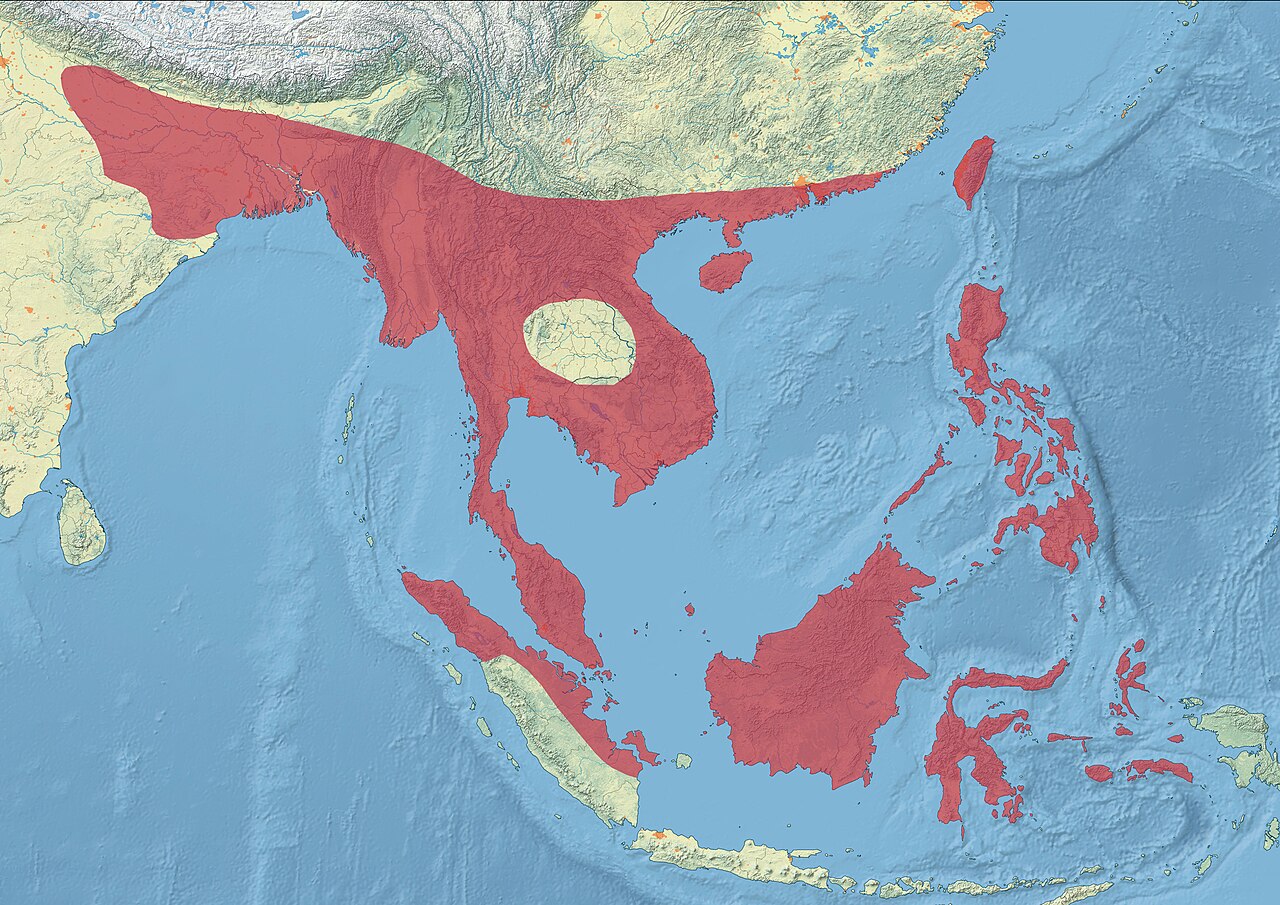
The chestnut munia or black-headed munia is a small passerine. It was formerly considered conspecific with the closely related tricoloured munia, but is now widely recognized as a separate species. This estrildid finch is a resident breeding bird in Bangladesh, Brunei, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Burma, Nepal, the Philippines, Singapore, Taiwan, Thailand, Vietnam and Hawaii. It also has been introduced to all the Greater Antilles and Martinique in the Caribbean.
Region
South and Southeast Asia
Typical Environment
Native across tropical Asia from the Indian subcontinent through mainland Southeast Asia to Indonesia, the Philippines, and Taiwan. It frequents open country with grasses, marsh edges, reedbeds, and agricultural landscapes, especially rice fields. The species readily adapts to human-modified habitats and village outskirts. It has been introduced to Hawaii and parts of the Caribbean, including the Greater Antilles and Martinique, where it occupies similar wet grassland and farmland niches.
Altitude Range
0–1800 m
Climate Zone
Tropical
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 4/5
Also called the black-headed munia, it often forms large flocks that forage in rice paddies and grasslands. Sexes are similar, while juveniles are buffy-brown without the dark head. It is a popular cagebird in parts of Asia and can become a local crop pest when congregating in fields.



Chestnut Munia in Azara, Assam

Adult

Chestnut munia nest. Nest is dome-shaped; entrance/exit point is visible

Adult
Temperament
social and active
Flight Pattern
short rapid wingbeats
Social Behavior
Highly gregarious outside the breeding season, forming flocks that move between feeding sites and roosts. Pairs are monogamous and build neat, globular grass nests concealed in tall grasses or reeds. Small loose colonies may occur where suitable nesting cover is abundant.
Migratory Pattern
Resident
Song Description
Song is a soft, twittering series of thin metallic notes interspersed with trills. Calls include gentle chips and wheezy contact notes used to keep flocks together.
Plumage
Compact finch with a glossy black head and throat contrasting with rich chestnut upperparts and flanks; belly varies from whitish to buff or pale chestnut depending on subspecies. The bill is stout and bluish-grey, and the tail is short and square. Juveniles are warm brown overall with a paler throat and lack the black head.
Diet
Primarily takes grass and sedge seeds, including rice and millet, which it husks efficiently with its strong conical bill. It also consumes small quantities of green shoots and occasionally small invertebrates, especially for nestlings. Flocks often exploit ripening grain, sometimes causing local agricultural damage.
Preferred Environment
Feeds on the ground and on seed heads in wet grasslands, paddy fields, and marsh margins. It also forages along ditches, weedy field edges, and village plots where seeding grasses are abundant.