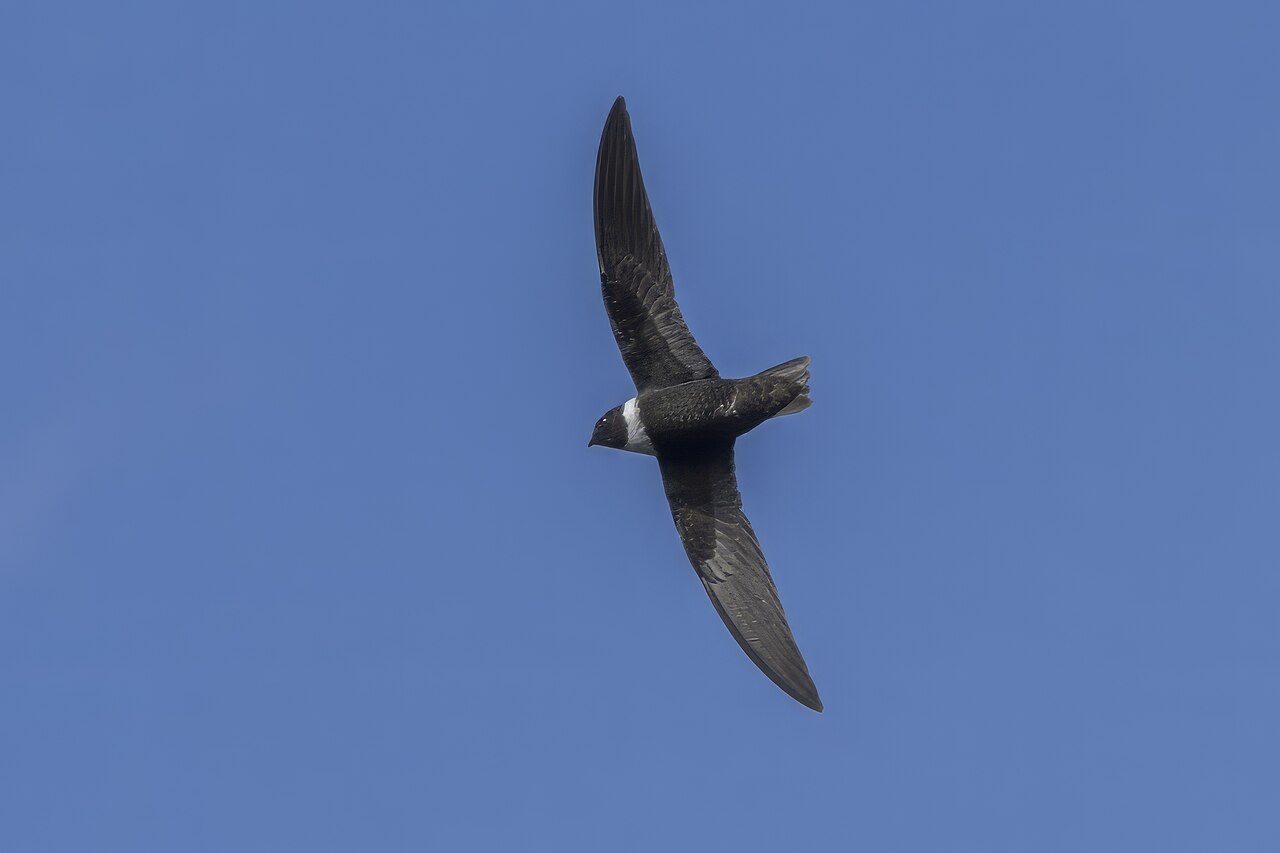

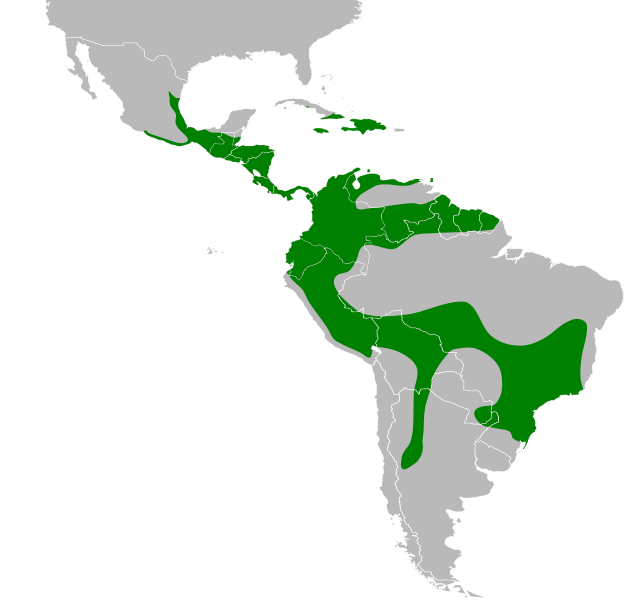
The white-collared swift is a species of bird in the subfamily Cypseloidinae of the swift family Apodidae. It is found in Mexico, Central America, the Greater and Lesser Antilles, Trinidad, and every mainland South American country except Chile.
Region
Neotropics
Typical Environment
Occurs from Mexico through Central America and the Caribbean to much of South America, absent only from a few southern regions. Favors rugged terrain with cliffs, gorges, and waterfalls where it roosts and nests in colonies. Common over montane and foothill forests but also ranges over open valleys and coastlines on islands. Frequently forages high above ridgelines, often far from nesting sites. Readily uses strong updrafts and storm fronts while feeding.
Altitude Range
Sea level to 3500 m
Climate Zone
Highland
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 1/5
One of the largest swifts in the Americas, the white-collared swift is famous for nesting on cliffs and behind waterfalls. Its long, scythe-like wings enable extremely fast, sustained flight as it forages high over mountains and valleys. Colonies often return to traditional roosts year after year. After storms or rains, flocks may gather to feed on swarming insects.



Temperament
social and active
Flight Pattern
powerful, fast flier with long sweeping arcs; soars on updrafts
Social Behavior
Typically seen in noisy flocks, especially near cliffs and over ridgelines. Nests colonially on vertical rock faces, often behind waterfalls or in caves, attaching shallow nests to moist rock. Likely monogamous with strong site fidelity to traditional colonies. Roosts communally outside the breeding season.
Migratory Pattern
Partial migrant
Song Description
Vocalizations are loud, piercing twitters and sharp screams given in flight, often heard before the birds are seen high overhead. Calls carry well across valleys and around waterfalls. Vocal activity increases around roosts and during group foraging.
Plumage
Mostly sooty-black with a bold, broad white collar encircling the upper breast and nape; plumage appears glossy in good light. Tail is slightly notched and wings are long and sickle-shaped.
Diet
An aerial insectivore that captures flying insects on the wing, including beetles, ants, termites, wasps, and flies. Often exploits bursts of swarming insects after rains and along storm fronts. Foraging occurs at various heights, frequently very high above terrain where updrafts concentrate prey.
Preferred Environment
Feeds over montane and foothill forests, river valleys, cliffs, and open countryside, frequently along ridgelines and near waterfalls. Also ranges over coastal areas and above towns when insects are abundant.