
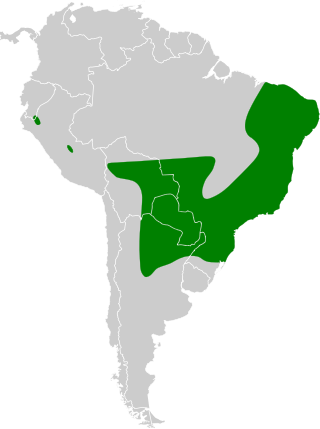
The Tataupa tinamou is a type of tinamou commonly found in dry forest in subtropical and tropical regions in southeastern South America.
Region
Southeast South America
Typical Environment
Occurs widely in eastern and central Brazil, extending into eastern Paraguay, northeastern Argentina, and parts of Bolivia. Prefers dry to semi-humid woodlands, caatinga, cerrado edges, secondary growth, and scrubby thickets. It stays close to dense undergrowth or leaf litter where it forages and shelters. Also uses forest edges and patches within agricultural mosaics if cover remains.
Altitude Range
Sea level to 1500 m
Climate Zone
Tropical
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 2/5
The Tataupa tinamou is a small, ground-dwelling bird that relies on camouflage and stillness to avoid predators. Males incubate clutches that may contain eggs from multiple females and also lead the chicks after hatching. Though a poor flier, it can burst into a short, explosive flight when flushed. Its clear, whistled call is often the best way to detect it in dense cover.



Egg, Collection Museum Wiesbaden
Temperament
shy and secretive
Flight Pattern
short rapid wingbeats; explosive flush over short distances
Social Behavior
Usually solitary or in pairs, sometimes small family groups. Nests on the ground in concealed sites lined with leaves. Males incubate and care for precocial chicks, often from a clutch laid by multiple females. Territorial calling is common at dawn and dusk.
Migratory Pattern
Resident
Song Description
A clear, plaintive two- to three-note whistle, often repeated at measured intervals. The call carries well through dry woodland and is frequently heard more than the bird is seen.
Plumage
Compact, uniformly brown to rufescent upperparts with fine dark barring, paler throat, and warmer rufous underparts. Feathers are smooth and close, aiding camouflage in leaf litter. Tail is very short and often hidden. Subtle contrast between greyish head and warmer body tones.
Diet
Eats small fallen fruits, seeds, tender shoots, and a variety of invertebrates such as insects and small arthropods. Forages by walking slowly and picking or scratching through leaf litter. Opportunistically takes berries and seeds during seasonal abundance. Its varied diet helps it persist in fragmented habitats.
Preferred Environment
Feeds on the forest floor within dry forests, scrub, and thicket edges, keeping close to dense cover. Often uses trails, clearings, and the edges of secondary woodland to search for fallen food items.