
The red-and-green macaw, also known as the green-winged macaw, is a large, mostly-red macaw of the genus Ara. It is popular in aviculture, and is the second most commonly kept macaw species after the Blue and Yellow. However, they are not as common in captivity as the Blue-and-yellow macaw, and are much more expensive; prices are often double that of the blue and gold.
Region
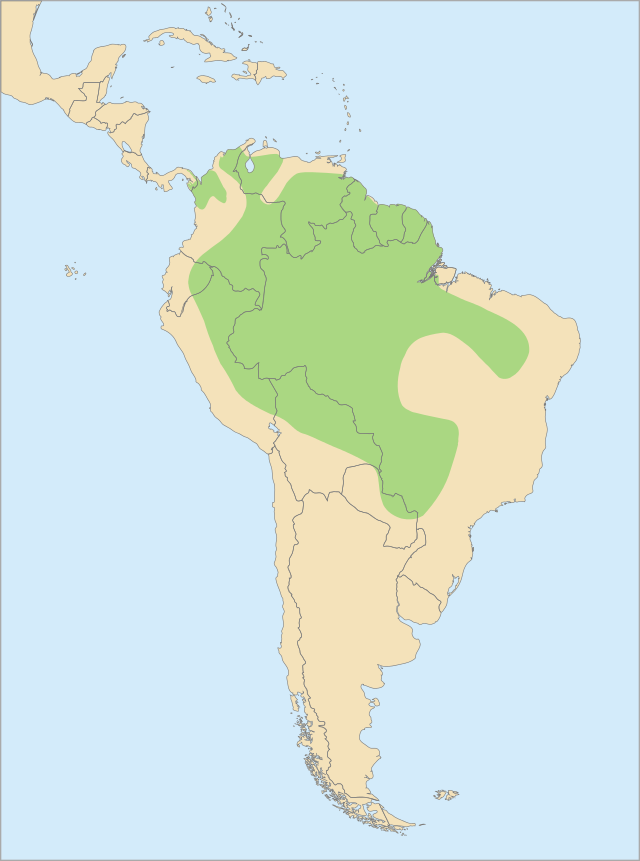
Amazon Basin and northern South America
Typical Environment
Inhabits humid lowland rainforests, gallery forests, and riverine woodlands from eastern Panama and northern South America through much of the Amazon Basin to northern Argentina and Paraguay. Most common along large rivers and floodplain forests where tall emergent trees provide nest cavities. Uses forest edges, clearings, and secondary growth when food is abundant. Frequently visits exposed riverbanks with clay licks. Locally extirpated in heavily deforested areas but remains widespread where suitable forest persists.
Altitude Range
Sea level to 1500 m
Climate Zone
Tropical
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 2/5
Also called the green-winged macaw, it’s among the largest macaws and is often confused with the scarlet macaw; look for the broad green band on the wings and fine red feather lines on the white face. It forms strong lifelong pair bonds and is frequently seen visiting riverbank clay licks to neutralize plant toxins. Powerful bills can crack hard nuts with ease, and their calls carry over long distances.






Temperament
social and intelligent, loud and assertive
Flight Pattern
strong flier with deep, steady wingbeats; occasional gliding
Social Behavior
Typically seen in pairs or small family groups, with larger flocks at feeding sites and clay licks. Strongly monogamous pairs maintain close contact in flight. Nests in large tree cavities, laying 2–3 eggs; both parents care for the young.
Migratory Pattern
Resident
Song Description
Loud, resonant squawks and raucous screeches that carry over long distances. Also gives grating contact calls and softer croaks within pairs at close range.
Plumage
Mostly deep red body with a broad green band across the upper wings transitioning to blue on the outer wings and tail; underwings show blue flight feathers. Bare white facial skin is crossed by fine lines of tiny red feathers.
Diet
Primarily eats fruits, seeds, and nuts, including hard palm nuts cracked with its powerful bill. Also takes berries, leaf buds, and flowers when available. Regularly visits mineral-rich clay licks, which may help detoxify secondary plant compounds and provide essential minerals.
Preferred Environment
Forages high in the forest canopy and along river margins where fruiting trees are concentrated. Frequently uses floodplain forests, gallery forests, and edges or clearings with fruiting palms and figs.