
The plumbeous ibis, also formerly called the blue ibis, is a large distinctive ibis species endemic to parts of central South America.
Region
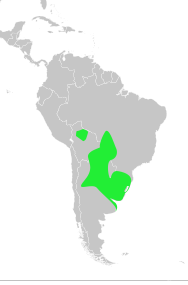
Pantanal and Gran Chaco of central South America
Typical Environment
Occurs in lowland wetlands of Bolivia, Paraguay, Brazil (especially the Pantanal and adjacent cerrado margins), and northern Argentina. Favors seasonally flooded grasslands, marshes, savanna wetlands, cattle pastures with standing water, and river floodplains. Often uses gallery woodland edges for roosting and nesting while feeding in open, wet meadows. It is largely sedentary but may make local movements tracking water levels across the flood cycle.
Altitude Range
0–800 m
Climate Zone
Subtropical
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 2/5
Also known as the blue ibis, the plumbeous ibis is a robust wetland ibis of the Pantanal and Gran Chaco. Its loud honking calls carry over long distances at dawn and dusk. It often forages in seasonally flooded pastures and marsh edges, helping control insects and other invertebrates. The long, decurved bill is specialized for probing soft mud and shallow water.


Temperament
wary but often conspicuous in open wetlands
Flight Pattern
strong flier with steady wingbeats and brief glides
Social Behavior
Usually seen in pairs or small family groups, sometimes forming loose flocks where feeding is good. Nests on trees near water, constructing bulky stick platforms. Likely monogamous, with both sexes participating in nest defense and care.
Migratory Pattern
Resident
Song Description
Vocalizations are loud, resonant honks and trumpeting calls that carry across wetlands. Calls are most frequent at dawn and dusk and during social interactions or territorial displays.
Plumage
Uniform leaden-grey body with slightly darker flight feathers; overall smooth, satiny appearance with subtle bluish sheen.
Diet
Feeds primarily on aquatic and terrestrial invertebrates such as insects, worms, snails, and crustaceans, and will also take small amphibians and other small prey. Probes soft mud and shallow water with its long bill to locate hidden prey. Opportunistically forages in wet pastures and along marsh margins where prey concentrates as water recedes.
Preferred Environment
Shallow wetlands, flooded grasslands, and muddy edges of lagoons and oxbows. Frequently uses seasonally inundated cattle pastures and ditches, especially in the Pantanal flood pulse.