
The Indian vulture or long-billed vulture is a bird of prey native to the Indian subcontinent. It is an Old World vulture belonging to the family of Accipitridae. It is a medium-sized vulture with a small, semi-bald head with little feathers, long beak, and wide dark colored wings. It breeds mainly on small cliffs and hilly crags in central India and south India.
Region
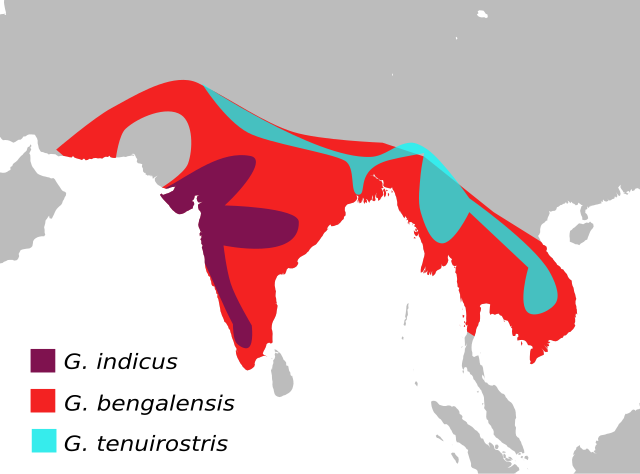
Indian Subcontinent
Typical Environment
Found mainly across central, western, and peninsular India, with pockets in adjoining Pakistan (especially Sindh) and parts of lowland Nepal. It frequents open country, dry plains, farmland mosaics, and semi-arid scrub interspersed with grazing lands. Nesting is typically on cliffs and rocky crags; it also roosts on large trees and pylons near villages and towns. Historically common around carcass dumps, it now persists patchily where vulture-safe practices are in place.
Altitude Range
0–1500 m
Climate Zone
Subtropical
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 1/5
Also called the long-billed vulture, it suffered catastrophic declines across South Asia in the 1990s–2000s due largely to veterinary diclofenac poisoning from livestock carcasses. Conservation actions now promote vulture-safe drugs (like meloxicam), establish breeding centers, and create Vulture Safe Zones. Its highly acidic stomach destroys many pathogens, making it an important natural sanitation agent.



Close-up of Indian vulture showing its long bill

Indian vulture in flight showing its wing span

An Indian vulture flying

Indian vultures nesting on a cliff

Indian vultures are slow and difficult breeders.

Jatayu sculpture in India
Temperament
social and gregarious at food sources
Flight Pattern
soaring glider
Social Behavior
Often forms loose colonies on cliffs and gathers in groups at carcasses, where a dominance hierarchy is evident. Pairs are monogamous and typically raise a single chick, nesting on ledges with a platform of sticks. Roosting is communal on cliffs, large trees, or pylons near foraging areas.
Migratory Pattern
Resident
Song Description
Generally silent away from nests and carcasses. At close range it produces grunts, hisses, and croaks during feeding interactions or at the nest.
Plumage
Sandy-brown to dark brown body with paler, often buff-washed underparts and a narrow pale ruff at the base of the neck; flight feathers are darker, creating contrast in the wings. The head and neck are largely bare and greyish, with sparse down. The bill is long, pale horn, and strongly hooked.
Diet
A specialized scavenger feeding almost exclusively on carrion, particularly livestock carcasses and occasionally wild ungulates. It tears skin and soft tissues with its long, hooked bill and feeds communally with other vultures. Its strong gastric acids help neutralize many pathogens, reducing disease spread around human settlements and grazing lands.
Preferred Environment
Forages over open countryside, grazing commons, village outskirts, and carcass dump sites. Uses thermals to soar widely between roosts, nesting cliffs, and feeding areas.