
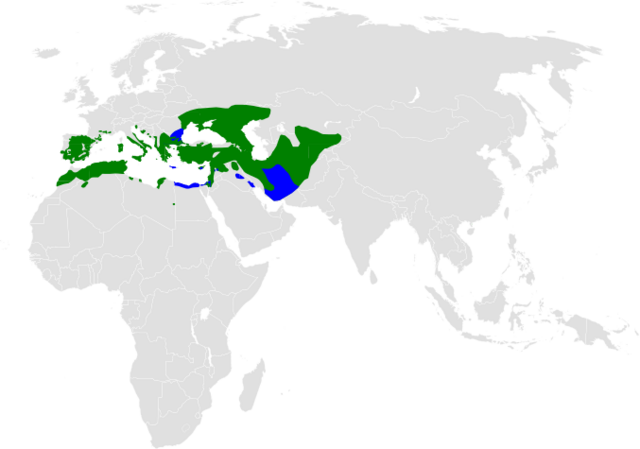
The calandra lark or European calandra-lark breeds in warm temperate countries around the Mediterranean and eastwards through Turkey into northern Iran and southern Russia. It is replaced further east by its relative, the bimaculated lark.
Region
Mediterranean Basin and Western-Central Asia
Typical Environment
Breeds across warm temperate regions around the Mediterranean and east through the Balkans, Turkey, the Caucasus, northern Iran, and into southern Russia and the Pontic–Caspian steppes. It occupies open country such as cereal fields, pastures, steppe grasslands, and fallow lands, often avoiding dense scrub and forests. During winter, some populations move to milder lowlands and coastal plains. It also uses airfields and extensive agricultural plains where ground cover is short.
Altitude Range
Sea level to 2000 m
Climate Zone
Temperate
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 2/5
The Calandra Lark is one of the largest larks in Europe and is renowned for its powerful, melodious song, often delivered in a high display flight. It shows striking black underwing coverts and bold black patches on the sides of the neck, making it easier to identify than many other larks. It favors open farmland and steppe and has benefitted historically from traditional cereal agriculture but can decline with intensive practices. It is replaced further east by the closely related Bimaculated Lark.



Eggs of Melanocorypha calandra MHNT
Temperament
social and active
Flight Pattern
strong flier with buoyant display flights, showing black underwings and white wing panels
Social Behavior
Generally pairs during the breeding season, nesting on the ground in a shallow scrape concealed by vegetation. Outside the breeding period it forms loose flocks, often mixing with other larks on stubble and pastures. Territorial singing males perform aerial displays over open fields.
Migratory Pattern
Partial migrant
Song Description
A loud, rich, and varied cascade of trills and whistles, often including mimicry of other birds. Males sing persistently from perches or while circling high overhead during display flights.
Plumage
Heavily streaked brown upperparts with paler edges and clean whitish underparts. Shows very large black patches on the sides of the neck and black underwing coverts visible in flight. Broad white trailing edge to the wings and white tips to the tail are conspicuous when flying.
Diet
Feeds mainly on seeds and grains from wild grasses and cultivated cereals, supplemented by green shoots and buds. In the breeding season it takes more invertebrates, including beetles, grasshoppers, and caterpillars, providing protein for nestlings. Forages by walking and gleaning on the ground, picking items from bare soil and low vegetation.
Preferred Environment
Open farmland, steppe, and lightly vegetated fields with patches of bare ground. Frequently uses stubble, fallow plots, and field margins where seed availability is high.