
The blue-and-yellow macaw, also known as the blue-and-gold macaw, is a large Neotropical parrot with a mostly blue dorsum, light yellow/orange venter, and gradient hues of green on top of its head. It is a member of the large group of neotropical parrots known as macaws. It inhabits forest, woodland and savannah of tropical Central and South America, as well as the island of Trinidad in the Caribbean. They are popular in aviculture because of their striking color, ability to talk, ready availability in the marketplace, and close bonding to humans. It is the most commonly kept macaw species in captivity worldwide as a pet or companion parrot and is also the cheapest among the large macaws. As of 2025, there are 1 million blue and gold macaws living in captivity worldwide, one of the highest population of any large parrot in captivity, such is the popularity of this bird.
Region
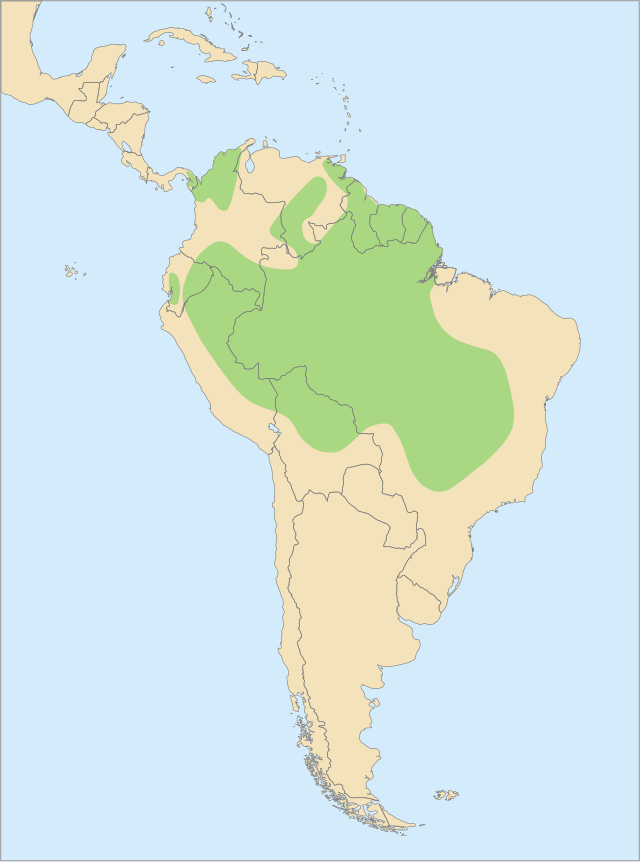
Tropical Central and northern South America
Typical Environment
Occurs from eastern Panama through northern South America east of the Andes, including Colombia, Venezuela, the Guianas, Trinidad, much of Brazil, eastern Peru, and northern Bolivia, with localized occurrences in Paraguay. It inhabits humid and seasonally flooded forests, gallery forests, forest edges, and savanna mosaics with palms. Birds often follow major river corridors and open forest canopy where tall emergent trees provide nesting cavities. They adapt to disturbed forest and secondary growth when large trees and food plants remain.
Altitude Range
Sea level to 1000 m
Climate Zone
Tropical
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 2/5
Also called the blue-and-gold macaw, it forms lifelong pair bonds and often flies in pairs or small family groups. Its powerful bill can crack the hardest palm nuts, and individuals frequent mineral-rich clay licks that may help neutralize plant toxins. Bare facial skin with fine black feather lines is unique to each bird, much like a fingerprint. Highly intelligent and capable of mimicry, it is popular in aviculture but requires substantial space and enrichment.



Ara ararauna – MHNT

20-day-old blue-and-gold macaw











Macaw in a bird fair in Italy
Temperament
social and active
Flight Pattern
strong flier with long, steady wingbeats; capable of swift, direct flight over forest and rivers
Social Behavior
Typically seen in pairs or small family groups, sometimes gathering in larger flocks at roosts and clay licks. Strongly monogamous with long-term pair bonds; pairs coordinate in flight and foraging. Nests in cavities of tall dead or living trees, laying a small clutch with prolonged parental care by both adults.
Migratory Pattern
Resident
Song Description
Vocalizations are loud, raucous screeches and squawks that carry over long distances. Birds also exchange grating contact calls and softer growls within pairs or groups.
Plumage
Brilliant blue upperparts with rich golden-yellow underparts; green wash on the crown. Bare white facial skin crossed by fine black feather lines and a black throat patch. Long tapered blue tail and blue flight feathers with darker tips.
Diet
Feeds mainly on fruits, seeds, and nuts, especially from palms and large-seeded trees. Regularly visits mineral-rich clay licks to ingest clay, likely for detoxifying plant compounds and obtaining minerals. May supplement with leaf buds and occasional other plant matter; travels widely between seasonal food sources.
Preferred Environment
Forages in the upper canopy and along forest edges and riverine corridors where fruiting trees are abundant. Frequently uses palm-dominated habitats and transitional woodland-savanna mosaics.