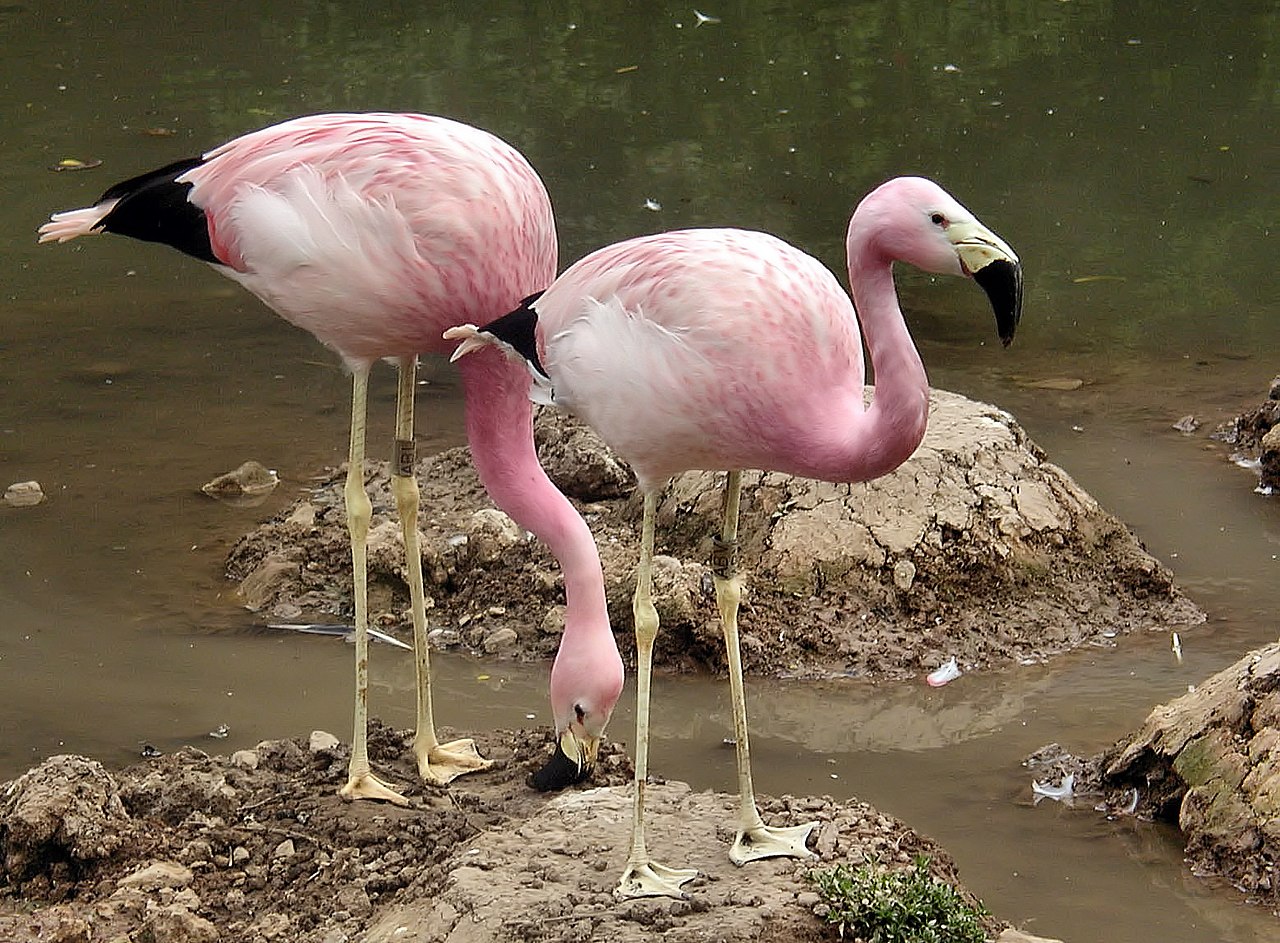

The Andean flamingo is a species of flamingo native to the Andes mountains of South America. Until 2014, it was classified in genus Phoenicopterus. It is closely related to James's flamingo, and the two make up the genus Phoenicoparrus. The Chilean flamingo, Andean flamingo, and James' flamingo are all sympatric, and all live in colonies.
Region
Andes Mountains
Typical Environment
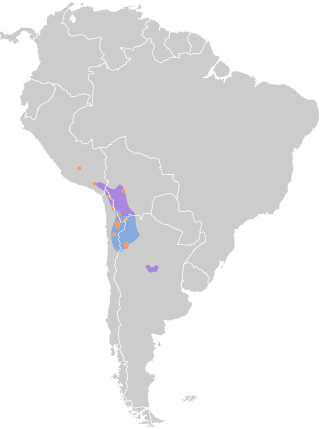
Found on the Altiplano of Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and northwestern Argentina, especially around large, shallow, saline and alkaline lakes and salt pans. Breeding occurs at remote, wind-swept lakes with extensive mudflats and islands. Outside the breeding season, birds may move among lakes as water levels and food availability change. They sometimes descend to lower-elevation wetlands during harsh winters but remain within the Andean region.
Altitude Range
2300–4600 m
Climate Zone
Highland
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 1/5
The Andean flamingo is the rarest of the world’s flamingos, confined to high-altitude saline lakes of the central Andes. It often forms mixed colonies with James’s and Chilean flamingos, building conical mud nests and laying a single egg. Its specialized filter-feeding targets microscopic algae and diatoms, making it highly sensitive to changes in water levels and salinity.



Andean flamingo (Phoenicoparrus andinus)

Andean flamingo foraging in a lake in Salar de Atacama, Chile



Temperament
social and active
Flight Pattern
strong flier with steady wingbeats; often flies in lines or V formations
Social Behavior
Highly gregarious, forming large mixed-species flocks and dense breeding colonies. Pairs are generally monogamous, building conical mud nests and laying a single egg, which both sexes incubate. Chicks gather in crèches guarded by adults while parents commute to feed.
Migratory Pattern
Partial migrant
Song Description
Vocalizations include nasal honks and goose-like braying calls, especially during flight and at colonies. Groups produce a constant chorus that helps maintain cohesion in large flocks.
Plumage
Pale pink overall with deeper rosy-pink wing coverts and contrasting black flight feathers visible in flight.
Diet
Specialized filter-feeder primarily consuming diatoms and microscopic algae; it also ingests small invertebrates and organic detritus. The bill’s lamellae sieve suspended particles as the bird sweeps its head side-to-side in shallow water. Diet composition shifts with lake productivity and salinity, often differing subtly from adjacent James’s and Chilean flamingos to reduce competition.
Preferred Environment
Feeds in shallow margins of high-altitude saline and alkaline lakes, salt pans, and brackish lagoons. Prefers areas with soft substrates and calm waters where fine particles remain suspended for efficient filtering.