
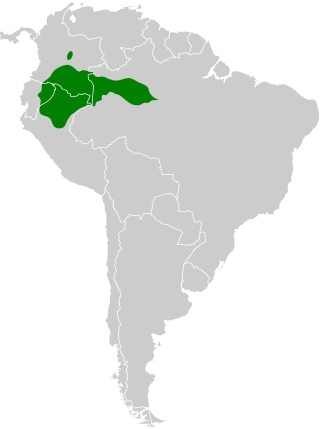
The white-cheeked antbird is an insectivorous bird in subfamily Thamnophilinae of family Thamnophilidae, the "typical antbirds". It is found in Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru.
Region
Western Amazon Basin
Typical Environment
Occurs in lowland and foothill tropical rainforests of Brazil (western Amazonia), Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. Prefers mature terra firme forest but also uses várzea and well-structured secondary forest with dense understory. Most frequently encountered near army-ant swarms on or just above the forest floor. Typically keeps to shaded, humid interiors rather than open edges.
Altitude Range
Sea level to 1200 m
Climate Zone
Tropical
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 1/5
An obligate follower of army ants, the white-cheeked antbird snatches insects and other small arthropods flushed by the swarms. Pairs often stay close together in the dim rainforest understory and can be quite secretive. Males show a striking white cheek patch contrasting with a dark head and body, making them distinctive in low light. Habitat loss is a concern in parts of its range, but the species is currently not considered globally threatened.



Temperament
shy and skulking
Flight Pattern
short rapid wingbeats, low and direct
Social Behavior
Usually found in pairs or family groups maintaining year-round territories. Strongly associated with army-ant swarms, where pairs keep close contact calls while foraging. Nests are placed low in dense vegetation; both sexes share incubation and chick rearing.
Migratory Pattern
Resident
Song Description
A clear, whistled series, often a descending sequence of notes delivered from low perches in the understory. Also gives sharp chips and chatter when attending ant swarms or interacting with mates.
Plumage
Compact antbird with smooth, close-fitting plumage; males are mostly dark with a bold white cheek, females more brownish with buffy tones. Overall appearance is cleanly marked rather than heavily streaked.
Diet
Primarily takes insects and other arthropods such as spiders and small beetles flushed by army ants. Will occasionally seize small vertebrates or larvae when available. Captures prey by quick sallies to the ground or low perches, often returning to a favored vantage.
Preferred Environment
Feeds on or just above the forest floor in dense, shaded understory near active army-ant swarms. Uses fallen logs, roots, and low branches as hunting perches.