
The western sandpiper is a small migratory shorebird. The genus name is from Ancient Greek kalidris or skalidris, a term used by Aristotle for some grey-coloured waterside birds. The specific mauri commemorates Italian botanist Ernesto Mauri (1791–1836).
Region
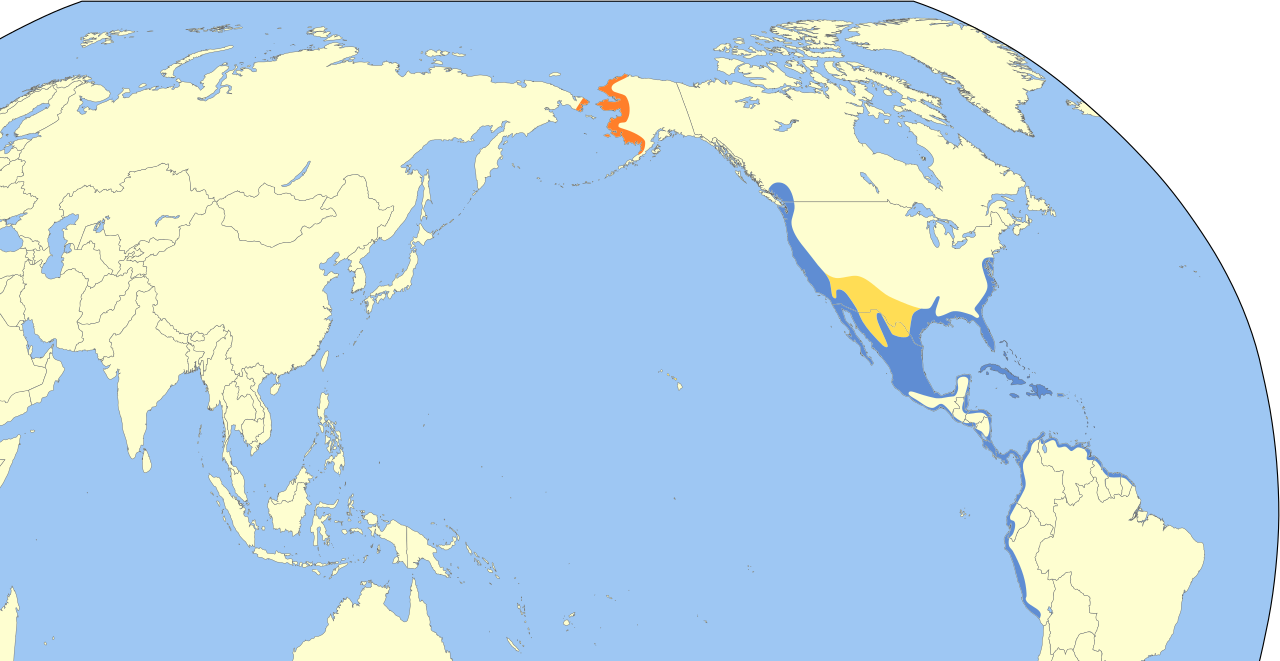
Pacific Flyway of the Americas
Typical Environment
Breeds on low Arctic tundra near the Bering Sea coast of Alaska and in adjacent Chukotka, Russia. During migration and winter it uses intertidal mudflats, estuaries, salt marsh edges, coastal lagoons, and sandy shores from the Pacific Northwest through Mexico to northern South America, and along parts of the Gulf of Mexico. Inland, it occasionally stops at flooded fields, lake margins, and river deltas. Key staging areas include the Copper River Delta and San Francisco Bay, where enormous mixed flocks gather.
Altitude Range
Sea level to 500 m
Climate Zone
Other
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 1/5
The western sandpiper is a small migratory shorebird that breeds in western Alaska and eastern Siberia and winters along the Pacific and Gulf coasts of the Americas. It is famous for forming vast, synchronized flocks at coastal stopover sites such as the Copper River Delta. Unusually for a shorebird, it often feeds on biofilm—microscopic algae and diatoms—by sweeping its tongue across mudflat surfaces. The genus name derives from Ancient Greek for grey waterside birds, and the species name honors Italian botanist Ernesto Mauri.


Temperament
social and active
Flight Pattern
short rapid wingbeats with agile, twisting flock maneuvers
Social Behavior
Highly gregarious outside the breeding season, forming tight, synchronized flocks that wheel over shorelines. Breeds on the ground in shallow tundra scrapes; both sexes typically incubate 3–4 eggs, and chicks are precocial. Pairs are generally seasonal monogamists, and parental roles can vary with males often leading broods after hatching.
Migratory Pattern
Seasonal migrant
Song Description
Calls are high, thin cheeps and trills, often given in rapid series during flock movements. Display songs in breeding season are soft, twittering trills. Vocalizations carry well over open mudflats and tundra.
Plumage
Breeding birds show rufous tones on the crown and scapulars with dark chevrons on the flanks; nonbreeding plumage is mostly gray above and white below with cleaner, plainer appearance. Juveniles display crisp scaly upperparts with rufous-edged feathers. Feathers are tight and sleek, suited for long-distance flight.
Diet
Feeds mainly on small invertebrates including polychaete worms, amphipods, copepods, small mollusks, and insect larvae. It is notable for grazing biofilm and diatoms from mudflat surfaces using a brush-tipped tongue. Diet composition shifts seasonally and by site, with more insect prey on breeding grounds and more marine invertebrates and biofilm on coasts.
Preferred Environment
Intertidal mudflats, estuaries, and shallow lagoon edges where soft substrates are exposed at low tide. On the breeding grounds it forages in wet tundra meadows, pond margins, and stream edges.