
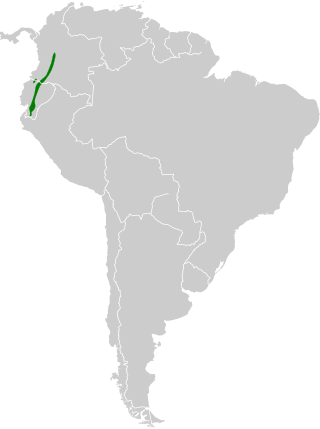
The viridian metaltail is a species of hummingbird in the "coquettes", tribe Lesbiini of subfamily Lesbiinae. It is found in Colombia and Ecuador.
Region
Andes Mountains
Typical Environment
Occurs along the Andes of southern Colombia and northern Ecuador, favoring elfin forest edges, high-montane shrublands, and páramo ecotones. It frequents flowering shrubs on steep slopes, ravines, and hedgerows near forest fragments. The species uses both natural páramo vegetation and disturbed edges where nectar sources persist. It defends rich flowering patches but may also follow routes between scattered blooms.
Altitude Range
2200–4100 m
Climate Zone
Highland
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 1/5
This high-Andean hummingbird takes its name from the male’s iridescent, metallic-looking tail. It often enters nightly torpor to conserve energy in cold montane habitats. By visiting tubular flowers, it is an important pollinator of páramo and cloud-forest plants. It typically remains year-round within its elevational band.



Temperament
territorial around rich nectar sources
Flight Pattern
short rapid wingbeats with agile hovering
Social Behavior
Typically solitary at flowers, with males aggressively defending feeding territories. Courtship involves aerial chases and display hovering. The female builds a small cup nest, usually placed on protected branches or banks, and incubates two eggs with little male assistance.
Migratory Pattern
Resident
Song Description
Vocalizations are high, thin tseet notes and rapid, insect-like trills delivered from low perches. Wing hum is audible at close range, especially during display chases.
Plumage
Overall metallic viridian-green with bronzy sheen; male shows a glittering green throat and an iridescent, slightly forked tail. Female tends to be duller with lighter mottling on the underparts and less intense throat sheen. Both sexes have a short, straight black bill and compact, tight plumage suited to high elevations.
Diet
Feeds primarily on nectar from high-Andean shrubs and flowers such as Fuchsia, Chuquiraga, and various Ericaceae and Melastomataceae. Supplements its diet with small arthropods, hawking them in short sallies or gleaning from foliage. Nectar provides energy while insects supply essential proteins, especially during breeding.
Preferred Environment
Forages along forest edges, páramo scrub, and flowering hedgerows where blooms are concentrated. Often uses sheltered ravines and ecotones that offer both nectar plants and perches.