
The southern brown kiwi, tokoeka, or common kiwi is a species of kiwi from South Island of New Zealand. Until 2000 it was considered conspecific with the North Island brown kiwi, and still is by some authorities.
Region
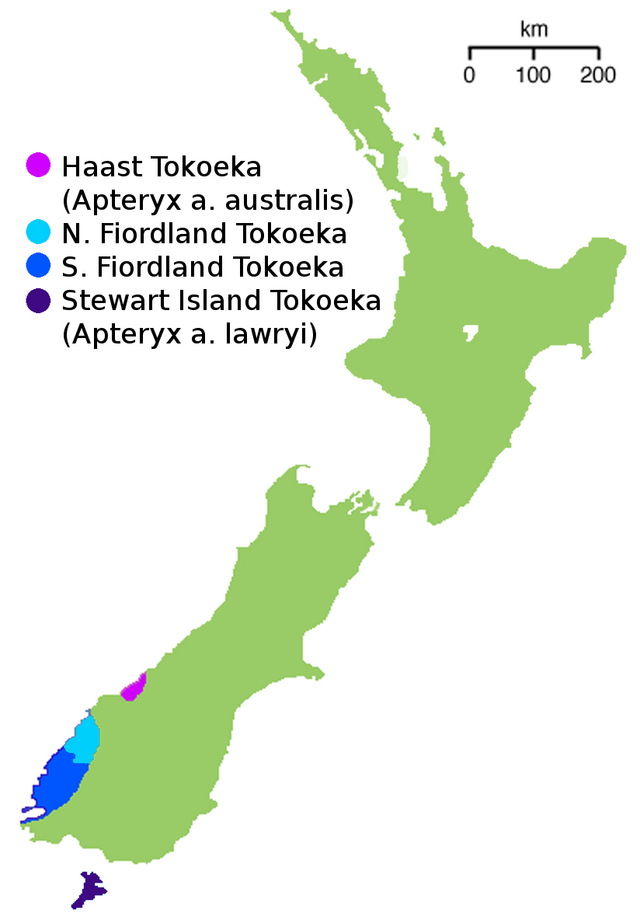
South Island and Stewart Island, New Zealand
Typical Environment
Found in temperate rainforests, dense podocarp–beech forests, coastal scrub, and subalpine shrublands. On Stewart Island/Rakiura, it also forages in open tussock and along forest edges. It uses burrows, hollow logs, and dense root tangles for daytime roosts and nesting. Habitat quality is strongly influenced by predator pressure and ground cover moisture, which supports invertebrate prey.
Altitude Range
Sea level to 1500 m
Climate Zone
Temperate
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 1/5
Also known as tokoeka, the southern brown kiwi is a flightless, nocturnal bird with hair-like feathers and a highly developed sense of smell, with nostrils at the tip of its long bill. It lays an exceptionally large egg relative to body size, and males perform most of the incubation. Pairs are typically monogamous and can remain together for many years.



Apteryx australis NML-VZ D180 Holotype from World Museum

Drawing of dissected specimen, with exposed muscles and wing-claw

Skeleton
Temperament
solitary and territorial
Flight Pattern
flightless; rapid running through dense undergrowth
Social Behavior
Typically forms long-term monogamous pairs that defend territories year-round. Nests are in burrows or natural cavities lined with vegetation. The male usually undertakes most incubation, and chicks are precocial, leaving the nest to feed soon after hatching.
Migratory Pattern
Resident
Song Description
At night, males give a series of high-pitched, ascending whistles often transcribed as 'kee-wee', while females respond with lower, harsher calls. Duets help maintain territory and pair bonds, and calls carry far through forested valleys.
Plumage
Coarse, hair-like feathers with loose texture; overall mottled to streaked brown with rufous tones.
Diet
Feeds primarily on soil invertebrates such as earthworms, beetle larvae, weta, and other insects, probing with its sensitive bill. It also takes spiders, small snails, and occasionally fallen fruit and seeds. The bird relies heavily on smell and tactile cues to locate prey beneath leaf litter and damp soil.
Preferred Environment
Forages on the forest floor, in leaf litter, along stream edges, and in soft, moist soils where invertebrates are abundant. On open tussock and pasture margins, it probes for worms and larvae during wetter nights.