
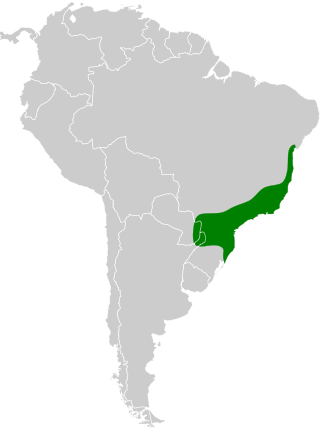
The green-headed tanager is a brightly colored bird found in the Atlantic forest in south-eastern Brazil, far eastern Paraguay, and far north-eastern Argentina.
Region
Atlantic Forest of southeastern South America
Typical Environment
Occurs in the Atlantic Forest of southeastern Brazil, extending into far eastern Paraguay and far northeastern Argentina (e.g., Misiones). It inhabits humid evergreen forests, secondary woodland, and forest edges, and readily uses gardens and orchards near forest. The species forages mainly in the mid to upper canopy but descends to lower levels at fruiting shrubs. It tolerates some habitat disturbance but depends on forested landscapes.
Altitude Range
Sea level to 1400 m
Climate Zone
Subtropical
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 1/5
This dazzling tanager is a hallmark of the Atlantic Forest, where it often joins mixed-species flocks to forage. Males are vividly colored while females and immatures are duller green, offering good camouflage in foliage. It frequently visits fruiting trees and even garden feeders, helping disperse seeds. Despite being common in parts of its range, it is sensitive to extensive forest loss.


Temperament
social and active
Flight Pattern
short rapid wingbeats
Social Behavior
Often travels in small groups and regularly joins mixed-species canopy flocks. Breeding pairs build a small cup nest in trees or dense shrubs, with a clutch typically of 2–3 eggs. Both parents participate in feeding the nestlings.
Migratory Pattern
Resident
Song Description
Soft, thin warbling phrases interspersed with high, sibilant chips. Calls are sharp and high-pitched contact notes used to keep in touch while foraging in flocks.
Plumage
Glossy green head, turquoise to blue body, and a contrasting black mantle with a narrow black nape collar. The rump is yellow to golden, with blue shoulder and wing panels edged in black. Females are greener and duller overall with less contrast; juveniles are largely greenish.
Diet
Feeds primarily on a variety of fruits and berries from native forest trees and shrubs. Supplements its diet with insects and other small arthropods gleaned from leaves and twigs. Occasionally sips nectar and will visit garden fruit feeders where available. Its fruit-eating habits contribute to seed dispersal in forest regeneration.
Preferred Environment
Forages mostly in the mid to upper canopy of humid forest and along edges. Also uses secondary growth, orchards, and well-vegetated gardens near forest. Frequently follows mixed-species flocks through fruiting trees.