
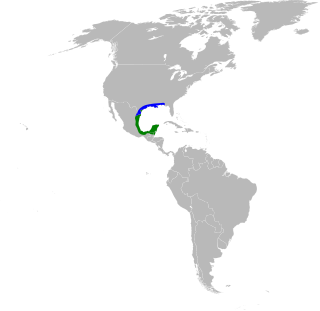
The buff-bellied hummingbird is a species of hummingbird in the "emeralds", tribe Trochilini of subfamily Trochilinae. It is found in Belize, Guatemala, Mexico, and the United States.
Region
Gulf Coast of Mexico and southern United States
Typical Environment
Occurs from the Yucatán Peninsula and eastern Mexico north into southern Texas, with nonbreeding dispersal along the U.S. Gulf Coast to Louisiana and occasionally farther east. It frequents coastal thickets, subtropical woodlands, second-growth scrub, and riparian edges. Gardens and parks with flowering shrubs and feeders are commonly used, especially in winter. In parts of Belize and Guatemala it inhabits lowland forest edges and clearings. It tends to remain near nectar-rich plants and perches conspicuously between feeding bouts.
Altitude Range
Sea level to 1500 m
Climate Zone
Subtropical
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 1/5
The buff-bellied hummingbird is an energetic, strongly territorial hummer noted for its warm buff underparts and rufous tail. It often expands northward along the Gulf Coast in winter, showing up at backyard feeders. Its bill is mostly red with a dark tip, a key feature for identification. Males perform short, buzzing display flights and give sharp chip notes around favored flower patches.



South Padre Island - Texas

Illustration from John Gould's 1861 monograph: A monograph of the Trochilidae, or family of humming-birds, Volume 5.

Temperament
territorial and alert
Flight Pattern
short rapid wingbeats with agile hovering
Social Behavior
Generally solitary outside of breeding, it aggressively defends nectar sources from other hummingbirds. Nests are small cups of plant down and spider silk placed on horizontal branches or in shrubs. Two eggs are typical, with the female solely incubating and caring for the young.
Migratory Pattern
Partial migrant
Song Description
Vocalizations are sharp chips and metallic ‘tik’ notes, often delivered in rapid series. Males produce buzzy trills and chase calls during territorial encounters; wings may add a faint mechanical hum in display flights.
Plumage
Iridescent green head and upperparts with a warm buff to cinnamon belly and flanks; tail and flight feathers show rufous tones with darker tips.
Diet
Takes nectar from tubular and brushy flowers such as salvias, hammelia, coralbean, and agaves. Also gleans or hawks tiny insects and spiders for protein, especially during breeding. Readily visits hummingbird feeders when available, showing dominance over smaller species.
Preferred Environment
Feeds along woodland edges, hedgerows, and dense coastal thickets with abundant flowering shrubs. In towns it favors gardens and parks with continuous blooms and sheltered perches.