
The Brazilian ruby is a species of hummingbird in the "brilliants", tribe Heliantheini, in the subfamily Lesbiinae. It is endemic to Brazil.
Region
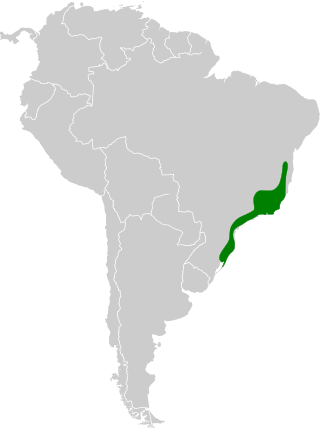
Atlantic Forest of southeastern Brazil
Typical Environment
Occurs from eastern and southeastern Brazil’s Atlantic Forest, including forest edges, secondary growth, and gardens. It favors montane and foothill zones but also uses disturbed habitats and shaded plantations. Birds frequently descend into lower elevations seasonally where flowers are abundant. The species is common in parks and rural areas with abundant flowering shrubs.
Altitude Range
300–2000 m
Climate Zone
Subtropical
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 1/5
The Brazilian ruby is a medium-sized hummingbird named for the male’s jewel-like ruby throat. It is an important pollinator of many Atlantic Forest plants and readily visits gardens and nectar feeders. Males are notably territorial around rich flower patches, often chasing away other hummingbirds.




Temperament
solitary and territorial
Flight Pattern
short rapid wingbeats and agile hovering
Social Behavior
Typically forages alone and males defend nectar territories vigorously. Nests are cup-shaped, built from plant down and spider silk on horizontal branches. Breeding occurs in the austral spring and summer, with females solely responsible for incubation and chick rearing.
Migratory Pattern
Resident
Song Description
Gives high-pitched chips and rapid twitters, often delivered while perched near feeding sites. Wingbeats produce a soft hum during close passes. Vocalizations intensify during territorial chases.
Plumage
Glittering green upperparts with a contrasting rufous tail; feathers appear iridescent in good light. Males show a brilliant ruby-red throat and upper breast; females have paler underparts with green mottling on the sides. Both sexes have a small whitish post-ocular spot and slightly forked rufous tail.
Diet
Feeds primarily on nectar from a variety of native and ornamental flowering plants, including bromeliads and tubular blossoms. Also takes small insects and spiders for protein, especially during the breeding season. It may hawk tiny insects in the air or glean them from foliage and webs. Readily visits artificial nectar feeders in gardens.
Preferred Environment
Forages along forest edges, clearings, and secondary growth where flowering shrubs are abundant. Often uses midstory and canopy flowers but will also feed at eye level in gardens and along roadsides.