
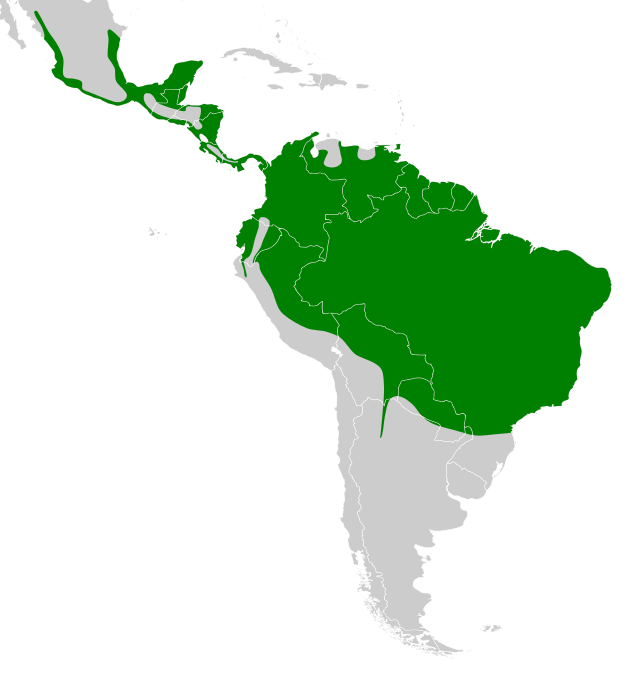
The bat falcon is a bird of prey in the family Falconidae, the falcons and caracaras. It is found in Mexico, Central America, Trinidad, and every mainland South American country except Chile and Uruguay.
Region
Neotropics
Typical Environment
Occurs from Mexico through Central America to much of South America, and on Trinidad. It favors forest edges, open woodland, riparian corridors, and savannas with scattered trees. The species often uses tall snags, palms, or utility structures as vantage perches near clearings and waterways. It tolerates some human-altered landscapes as long as suitable perches and foraging openings are present.
Altitude Range
0–2500 m
Climate Zone
Tropical
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 1/5
Despite its name, the bat falcon also preys on small birds and large flying insects, but it is adept at catching bats on the wing at dusk. It often hunts from an exposed perch, launching rapid, precise sallies over forest edges and rivers. Pairs typically defend territories year-round and nest in tree cavities or cliff crevices.



F.r. petoensisOrange Walk District, Belize

Temperament
solitary and territorial
Flight Pattern
short rapid wingbeats with swift, direct dashes and sudden stoops
Social Behavior
Usually seen alone or in pairs perched prominently while scanning for prey. Pairs are monogamous and defend territories; nesting is typically in tree cavities, old woodpecker or parrot holes, or cliff crevices, with minimal nest lining. The species is attentive to nest sites and may reuse favorable perches for hunting.
Migratory Pattern
Resident
Song Description
Vocalizations are sharp, high-pitched kek-kek-kek or kik notes, often given in rapid series. Calls carry well over forest edges and during territorial or pair contact displays. Nesting birds may give harsher chatter when disturbed.
Plumage
Glossy dark slate-black upperparts with a contrasting white throat and upper chest, and rich rufous lower underparts and thighs. The breast may show fine dark barring and the tail is dark with narrow pale bands. Feathers are tight and sleek, aiding swift flight.
Diet
Primarily hunts small bats at dusk, but also takes small birds, large insects such as dragonflies and beetles, and occasionally small lizards. Prey is often seized on the wing during swift sallies from a perch. It may dismember larger prey on a perch before feeding, swallowing insects whole in flight.
Preferred Environment
Forages along forest margins, over rivers and lagoons, and above clearings where aerial prey is concentrated. Perches on tall snags, emergent trees, or human-made structures that provide clear lines of sight.