
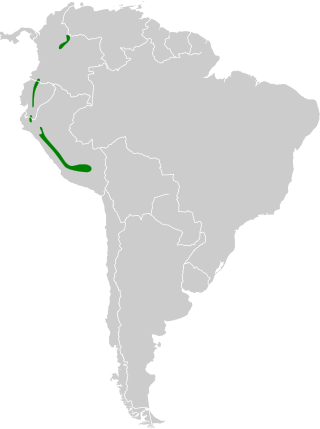
The black-tailed trainbearer is a species of hummingbird in the family Trochilidae. It is found between 2500 and 3800m in Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist montane forest, subtropical or tropical high-altitude shrubland, and heavily degraded former forest.
Region
Northern Andes
Typical Environment
Occurs along the Andes in Colombia, Ecuador, and northern Peru, primarily on montane slopes and high inter-Andean valleys. It favors edges of moist montane forests, high-altitude scrub, and hedgerows. The species readily uses disturbed areas and gardens with abundant tubular flowers. It is typically found in open or semi-open habitats near shrubby cover where nectar plants are concentrated.
Altitude Range
2500–3800 m
Climate Zone
Highland
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 1/5
This striking hummingbird is named for the male’s extraordinarily long, black tail 'train,' which can be longer than the rest of its body. It frequents shrubby highland habitats and even gardens where flowering shrubs are abundant. Like most hummingbirds, it fiercely defends rich nectar sources and supplements its diet with tiny insects for protein.



Temperament
solitary and territorial
Flight Pattern
short rapid wingbeats; agile hoverer
Social Behavior
Usually encountered singly, defending rich flower patches vigorously against other hummingbirds. Courtship involves conspicuous perching and tail displays by males. Nests are small cup structures of plant fibers bound with spider silk, placed on branches or in shrubs. Clutches typically consist of two white eggs.
Migratory Pattern
Partial migrant
Song Description
Vocalizations are thin, high-pitched chips and rapid twitters given during foraging and territorial chases. Males may add buzzy, chattering notes during displays, often interspersed with audible wing whirs in close flight.
Plumage
Glossy green upperparts with metallic sheen; males with very long, narrow, deeply forked black tail. Underparts greenish to grayish; females show pale whitish underparts with green spotting or streaking and a shorter, notched dark tail.
Diet
Feeds primarily on nectar from tubular flowers of Andean shrubs and ornamentals such as Fuchsia and Salvia. It also gleans or hawks tiny insects and spiders, especially during breeding for added protein. The long tail does not hinder its ability to hover precisely at blossoms.
Preferred Environment
Forages along forest edges, high-altitude scrub, hedgerows, and gardens where flowering plants are clustered. Often uses perches near nectar sources to watch and defend feeding territories.