
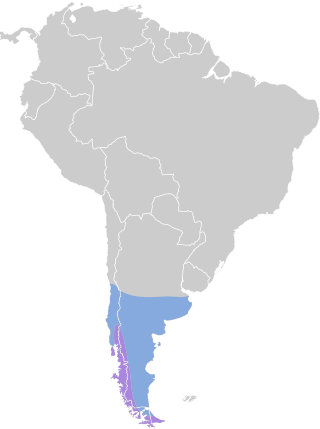
The ashy-headed goose is a species of waterfowl in tribe Tadornini of subfamily Anserinae. It is found in Argentina and Chile.
Region
Southern Andes and Patagonia
Typical Environment
Breeds in southern Chile and Argentina, mainly in Andean foothills and Patagonian uplands, and moves to lower elevations and open lowlands in winter. It favors freshwater lakes, marshy meadows, and damp grasslands adjacent to woodland. During the non-breeding season it often uses pastures and agricultural fields to graze. It generally avoids coastal shores compared with some related species. Local movements can be both latitudinal and altitudinal following food availability.
Altitude Range
0–1800 m
Climate Zone
Temperate
Ease of Keeping
Beginner friendly: 2/5
The ashy-headed goose is a South American sheldgoose that favors forested lakes and grassy clearings, often within southern beech (Nothofagus) zones. Sexes look similar, unlike some close relatives, making plumage cues subtle in the field. Outside the breeding season it gathers in small flocks to graze, and its flight reveals bold white wing patches. Males tend to whistle while females give harsher cackles.






Temperament
wary but social
Flight Pattern
strong flier with direct, rapid wingbeats
Social Behavior
Typically seen in pairs during the breeding season and in small to medium flocks outside it. Pairs are monogamous and nest on the ground near water, concealed in grass or low shrubs. Broods are attended by both parents, and family groups often remain cohesive after fledging.
Migratory Pattern
Partial migrant
Song Description
Vocalizations include mellow whistles and soft honks; males give clearer whistles, while females produce harsher cackling notes. Calls carry over open water and meadows, especially when alarmed or in flight.
Plumage
Ashy-gray head and neck with a fine white eye ring; body finely barred black and white on the flanks and back; breast often tinged warm brown; conspicuous white patches in the wing visible in flight.
Diet
Primarily grazes on grasses, sedges, and herbs, clipping short swards much like other geese. It also takes shoots, leaves of aquatic plants, and occasionally seeds. In agricultural areas it may feed on pasture and spillover crops. Animal matter is minimal and incidental.
Preferred Environment
Feeds in damp meadows, lake margins, and grassy clearings near freshwater. During winter it often uses open pasturelands and river floodplains where tender growth is abundant.